Introduction
Finite Element Analysis (FEA) has become a cornerstone of modern mechanical engineering, enabling precise simulation of complex structures before any prototype hits the shop floor. From automotive components to aerospace assemblies and heavy machinery, FEA Structural Analysis Services allow engineers to predict stress, strain, deformation, and failure modes with unmatched accuracy.
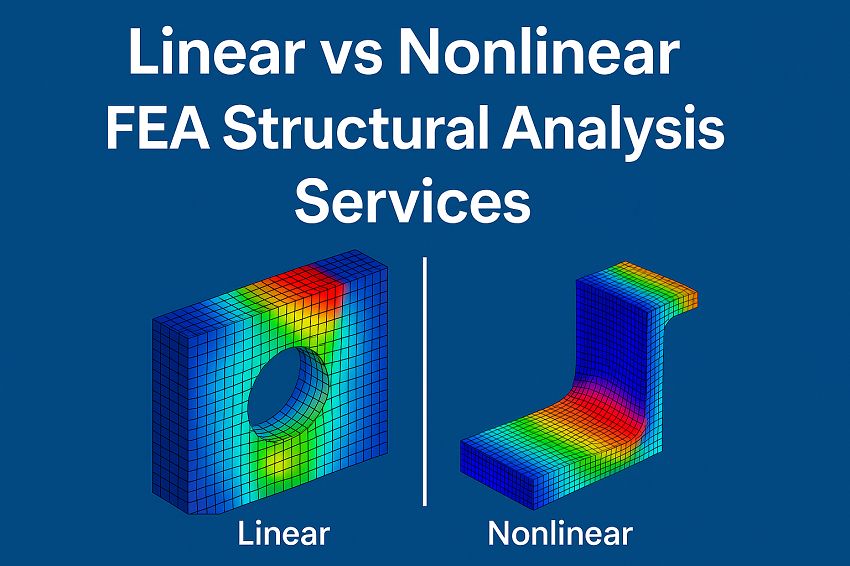
Among its core techniques, Linear and Nonlinear FEA analysis play distinct roles depending on material behavior, load conditions, and boundary complexities. Understanding these differences is key to selecting the right simulation approach for your product design.
What is FEA Structural Analysis
FEA Structural Analysis divides a physical structure into smaller, manageable elements (finite elements). Mathematical equations define each element’s response to external forces, pressure, and temperature. The results are then combined to predict how the entire structure behaves under specific loading conditions.
Engineers and product designers use FEA to:
- Predict stress distribution and displacement
- Identify critical failure zones
- Optimize geometry and material selection
- Minimize testing costs and development time
According to a 2024 report by MarketsandMarkets, the global FEA market size is expected to grow from USD 3.1 billion in 2023 to USD 5.7 billion by 2028, at a CAGR of 12.8%, driven by the demand for virtual testing and digital twins (https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/).
Linear vs Nonlinear FEA Analysis – The Core Difference
|
Aspect |
Linear FEA |
Nonlinear FEA |
|
Material Behavior |
Assumes linear elastic materials |
Handles plasticity, hyperelasticity, viscoelasticity |
|
Geometry Changes |
Small deformations |
Large deformations and rotations |
|
Boundary Conditions |
Linear and constant |
Vary with time or load magnitude |
|
Computation Time |
Faster and simpler |
Time-intensive and iterative |
|
Applications |
Shafts, beams, pressure vessels |
Rubber seals, crash simulations, metal forming |
Linear FEA Structural Analysis – When and Why to Use
Linear FEA assumes that the structure’s response (deformation or stress) is directly proportional to the applied load.
Use Cases
- Small strain and deflection problems
- Uniform material properties
- Stiff metallic components
Common Applications
- Machine frames and housings
- Structural beams and supports
- Bolted joints and pressure vessels
Advantages
- Quick and cost-effective simulation
- Ideal for early-stage design validation
- Simple interpretation of results
Limitations
- Inaccurate for high-deformation or contact problems
- Cannot handle material plasticity or boundary shifts
Nonlinear FEA Structural Analysis – Handling Real-World Complexities
Nonlinear FEA captures the true physical behavior of materials and structures when loads, geometry, or boundary conditions become complex. It accounts for nonlinear stress-strain relationships, large deformations, and contact interactions.
Types of Nonlinearities
- Material Nonlinearity – When stress is not proportional to strain (plasticity, hyperelasticity).
- Geometric Nonlinearity – When large deformations alter the structure’s stiffness.
- Boundary Nonlinearity – When contacts or supports change during loading.
Applications
- Crashworthiness and impact analysis
- Rubber seals and gaskets
- Metal forming and stamping processes
- Composite material testing
- Welded and bolted joints under cyclic loads
Advantages
- Simulates real-world loading conditions
- Accurate prediction of material failure
- Improves product reliability and safety
Limitations
- High computation time
- Requires expert setup and validation
When to Choose Linear or Nonlinear FEA Services
|
Scenario |
Recommended Analysis |
|
Design validation with low stress |
Linear |
|
High deformation materials like rubber |
Nonlinear |
|
Impact, crash, or forming analysis |
Nonlinear |
|
Small load variations in metals |
Linear |
|
Frictional contact or material yielding |
Nonlinear |
Example:
In a study by NASA Technical Reports, advanced nonlinear FEA reduced physical test iterations by 42%, cutting prototyping costs significantly (https://ntrs.nasa.gov/).
Benefits of Outsourcing FEA Structural Analysis Services
Outsourcing to specialized providers ensures access to advanced simulation tools like ANSYS, Abaqus, SolidWorks Simulation, and COMSOL Multiphysics.
Key Advantages
- Experienced analysts reduce trial-and-error
- Reduced design cycle time
- Scalable computation with HPC systems
- Cost-effective compared to in-house setup
- Reliable documentation for ISO and ASME compliance
Best Practices for Accurate FEA Simulation
- Use high-quality CAD geometry and mesh refinement
- Validate with physical test correlation
- Apply realistic boundary conditions and constraints
- Consider material data from standards (ASTM, SAE)
- Run sensitivity analysis to assess load impact
- Always perform result verification and convergence checks
Statistics That Highlight the Value of FEA
- Up to 30% reduction in product development cost through simulation-driven design (Source: Siemens PLM Report).
- 50% faster design cycles achieved by companies adopting early-stage FEA validation (ANSYS User Conference 2023).
- 40% improvement in fatigue life in components optimized using nonlinear FEA (Altair Engineering Research).
FAQ Section
Q1. What is the main difference between linear and nonlinear FEA?
Linear FEA assumes proportional load-deformation relationships, while nonlinear FEA accounts for complex behaviors like material yielding, large deformations, and contact effects.
Q2. How long does a typical FEA project take?
A linear analysis can be completed within hours, whereas a detailed nonlinear analysis might take several days depending on model complexity and solver convergence.
Q3. Can nonlinear FEA predict failure accurately?
Yes, when set up correctly with accurate material properties and boundary conditions, nonlinear FEA can closely predict real-world failure points.
Q4. What software tools are most used for FEA Structural Analysis?
ANSYS, Abaqus, NASTRAN, SolidWorks Simulation, and COMSOL are widely used across industries.
Q5. How often should a company perform FEA simulation?
FEA should be integrated at every critical design phase—concept, prototype validation, and final testing—to ensure reliability before mass production.
Conclusion
Whether it’s evaluating simple metallic structures or complex elastomeric components, FEA Structural Analysis Services are indispensable for modern mechanical design. While Linear FEA offers fast, cost-effective validation for small-deformation cases, Nonlinear FEA brings precision and reliability for complex real-world challenges.
Choosing the right partner with domain expertise ensures accurate results, faster product development, and compliance with industry standards — ultimately leading to safer and more efficient designs.

Krupal Patel
Krupal Patel is the CEO of Neocent Engineering Pvt. Ltd., Ahmedabad, specializing in advanced engineering solutions. With over 8 years of expertise in Product Design, FEA, CFD, and ASME-BPVC stress analysis, he has successfully delivered high-precision projects across pressure vessels, piping, and structural systems.
